Cloud web server hosting has revolutionized the way websites and applications are deployed and managed. This modern approach offers a flexible, scalable, and cost-effective alternative to traditional hosting methods, empowering businesses of all sizes to thrive in the digital landscape.
Cloud web server hosting utilizes a network of interconnected servers, allowing for dynamic resource allocation and efficient utilization. This infrastructure provides a range of benefits, including increased reliability, enhanced security, and the ability to scale resources on demand to accommodate fluctuating traffic and growth. Whether you’re a seasoned developer or just starting your online journey, understanding the intricacies of cloud web server hosting is crucial for building a robust and successful online presence.
Introduction to Cloud Web Server Hosting
Cloud web server hosting is a type of web hosting where resources are provided over a network of data centers, rather than a single physical server. It leverages the power of virtualization and distributed computing, allowing for scalable and flexible web hosting solutions.
Cloud web server hosting offers several advantages over traditional hosting methods. It provides increased flexibility, scalability, and reliability, making it an attractive option for businesses of all sizes.
Types of Cloud Hosting Services, Cloud web server hosting
Cloud hosting services are available in various forms, each offering different levels of resources and control. The most common types of cloud hosting services include:
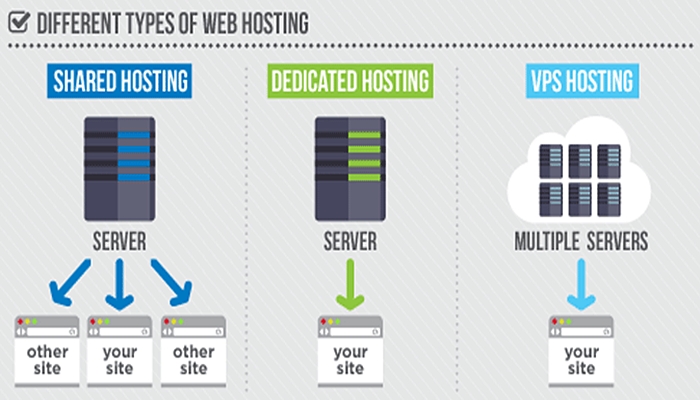
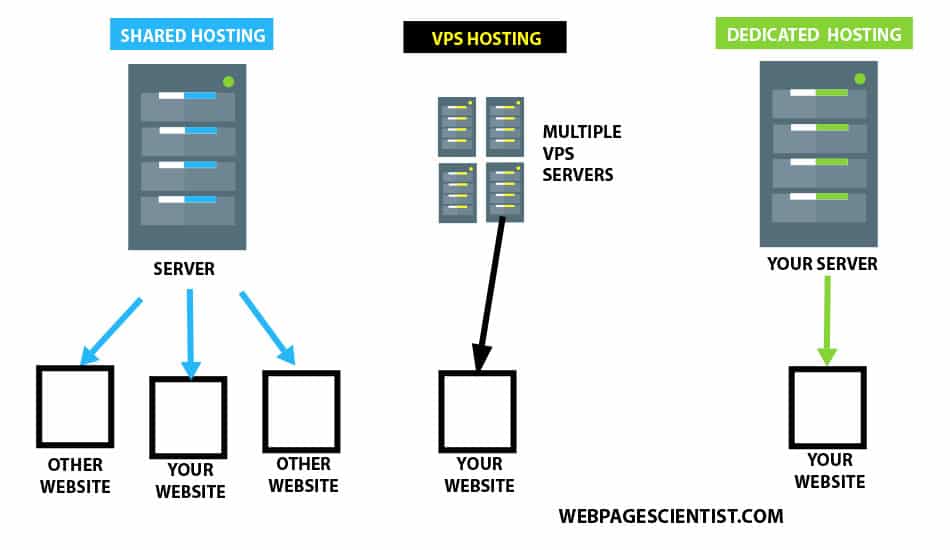
- Shared Hosting: In shared hosting, multiple websites share the resources of a single server. This is the most affordable option, but it also offers the least control and performance.
- VPS Hosting: VPS hosting provides a virtualized environment on a physical server, offering more resources and control than shared hosting. It is a good option for websites with moderate traffic and resource requirements.
- Dedicated Hosting: Dedicated hosting provides an entire physical server dedicated to a single website. This offers the highest level of control, performance, and security, but it is also the most expensive option.
Choosing the Right Cloud Hosting Provider
Choosing the right cloud hosting provider is a crucial decision for any website or application. With so many options available, it can be overwhelming to know where to start. This section will explore key factors to consider, compare popular providers, and discuss the pros and cons of different plans and pricing models.
Key Factors to Consider
It is essential to consider various factors when choosing a cloud hosting provider to ensure that the chosen provider meets your specific needs.
- Reliability: Reliability is paramount, as downtime can significantly impact your business. Look for providers with a proven track record of uptime and robust disaster recovery plans.
- Performance: Performance is critical for delivering a smooth user experience. Choose a provider with a strong global network infrastructure, fast processing speeds, and sufficient bandwidth.
- Security: Security is essential to protect your data and applications from cyber threats. Look for providers that offer robust security features, such as firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and data encryption.
- Scalability: Scalability is crucial for handling fluctuations in traffic and growth. Choose a provider that offers flexible scaling options, allowing you to easily adjust resources as needed.
- Cost: Cost is a significant consideration. Compare pricing models, features, and value for money across different providers.
- Customer Support: Responsive and reliable customer support is essential for resolving issues and getting help when needed. Look for providers with 24/7 support options and a proven track record of customer satisfaction.
Popular Cloud Hosting Providers
Several popular cloud hosting providers dominate the market, each offering a unique set of features and benefits.
- Amazon Web Services (AWS): AWS is the world’s leading cloud platform, offering a wide range of services, including compute, storage, networking, database, analytics, and more. It boasts a vast global infrastructure, high reliability, and extensive documentation and support resources. However, its complexity and pricing can be challenging for beginners.
- Microsoft Azure: Azure is another major cloud platform, offering a comprehensive suite of services similar to AWS. It is known for its strong integration with Microsoft products and services, making it a good choice for businesses using Microsoft technologies. Azure also offers a generous free tier, making it an attractive option for startups and small businesses.
- Google Cloud Platform (GCP): GCP is a rapidly growing cloud platform known for its innovative services, such as BigQuery for data analytics and Kubernetes for container orchestration. It also offers competitive pricing and a user-friendly interface. However, GCP’s ecosystem is not as mature as AWS or Azure.
Cloud Hosting Plans and Pricing Models
Cloud hosting providers offer various plans and pricing models to suit different needs and budgets.
- Pay-as-you-go: This model charges you based on the resources you consume, such as CPU, memory, and storage. It is ideal for applications with fluctuating resource demands.
- Reserved Instances: This model offers discounted pricing for committing to a specific amount of resources for a set period. It is suitable for applications with consistent resource requirements.
- Spot Instances: This model provides access to unused computing capacity at significantly lower prices. However, it is less reliable than other models because instances can be reclaimed with short notice.
Setting Up and Managing a Cloud Web Server
Setting up and managing a cloud web server can seem daunting, but with the right knowledge and tools, it’s a straightforward process. This section will guide you through the steps involved, from creating an instance to configuring security and monitoring performance.
Creating a Cloud Server Instance
Creating a cloud server instance is the first step in setting up your cloud web server. This involves choosing the right cloud provider, selecting an instance type, and configuring the operating system.
- Choose a Cloud Provider: There are several popular cloud providers available, each offering different features and pricing models. Some popular options include Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP). Consider factors like cost, features, and geographic location when making your choice.
- Select an Instance Type: Once you’ve chosen a provider, you’ll need to select an instance type. Instance types vary in terms of CPU, RAM, storage, and network capabilities. Choose an instance type that meets the requirements of your website or application.
- Configure the Operating System: You’ll need to choose an operating system (OS) for your instance. Popular choices include Linux distributions like Ubuntu or CentOS, or Windows Server. The OS you choose will depend on the requirements of your website or application.
Configuring Security
Security is paramount when setting up a cloud web server. You need to implement measures to protect your server from unauthorized access and cyber threats.
- Firewall: Configure a firewall to block unauthorized access to your server. You can use a software firewall like iptables on Linux or Windows Firewall on Windows Server. A firewall acts as a barrier, blocking unwanted traffic and allowing only authorized connections.
- Security Groups: Cloud providers often offer security groups, which act as virtual firewalls. You can create rules to control inbound and outbound traffic based on IP addresses, ports, and protocols.
- Password Management: Use strong, unique passwords for all accounts on your server. Consider using a password manager to securely store and manage your passwords.
- Regular Security Updates: Keep your operating system and software up to date with the latest security patches to mitigate vulnerabilities.
Common Web Server Software
Web server software is responsible for handling requests from web browsers and delivering web pages. Two popular options are Apache and Nginx.
- Apache: Apache is a widely used open-source web server known for its stability and extensive features. It’s highly configurable and supports various modules for extending its functionality.
- Nginx: Nginx is another popular open-source web server known for its high performance and efficiency. It’s often used for handling static content, reverse proxying, and load balancing.
Managing and Monitoring Cloud Web Servers
Managing and monitoring your cloud web server is essential for ensuring its availability, performance, and security. Several tools and techniques can help you manage and monitor your server effectively.
- Command-Line Interface (CLI): Cloud providers offer CLIs to interact with your servers and manage resources. CLIs provide a powerful way to automate tasks and manage your server remotely.
- Web-Based Consoles: Most cloud providers offer web-based consoles to manage your servers, instances, and other resources. These consoles provide a user-friendly interface for managing your cloud infrastructure.
- Monitoring Tools: Monitoring tools help you track the performance and health of your server. They can alert you to issues like high CPU usage, disk space shortages, or network problems. Popular options include Datadog, New Relic, and Prometheus.
Security Considerations in Cloud Hosting
While cloud hosting offers numerous benefits, it also introduces new security challenges. It’s crucial to understand these threats and implement robust security measures to protect your data and applications.
Security Threats Specific to Cloud Environments
Cloud environments are susceptible to various security threats, including:
- Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) Attacks: These attacks aim to overwhelm a server with traffic, making it unavailable to legitimate users. DDoS attacks can be particularly damaging in cloud environments, as they can target multiple servers or even the entire cloud infrastructure.
- Data Breaches: Cloud storage services can be targeted by attackers seeking to steal sensitive data. Data breaches can occur through vulnerabilities in the cloud provider’s security infrastructure, misconfigurations, or weak security practices by users.
- Malware and Viruses: Malicious software can infiltrate cloud environments through infected files, vulnerable applications, or compromised user accounts. Malware can steal data, disrupt operations, or spread to other systems.
- Insider Threats: Employees or contractors with access to cloud resources can pose a significant security risk. Insider threats can involve data theft, unauthorized access, or malicious activities.
- Misconfigurations: Improperly configured cloud services or applications can create security vulnerabilities that attackers can exploit. Misconfigurations can involve weak passwords, open ports, or missing security patches.
Best Practices for Securing Cloud Web Servers
Implementing strong security measures is essential to mitigate the risks associated with cloud hosting. Here are some best practices:
- Strong Passwords and Multi-Factor Authentication: Use strong, unique passwords for all cloud accounts and enable multi-factor authentication (MFA) to add an extra layer of security. MFA requires users to provide two or more forms of identification, making it more difficult for attackers to gain unauthorized access.
- Firewalls and Intrusion Detection Systems: Deploy firewalls to block unauthorized access to your cloud servers and use intrusion detection systems (IDS) to monitor network traffic for suspicious activity. Firewalls act as a barrier between your servers and the outside world, while IDS can detect and alert you to potential attacks.
- Regular Security Audits and Patching: Conduct regular security audits to identify and address vulnerabilities in your cloud infrastructure. Keep all software and operating systems up to date with the latest security patches to fix known vulnerabilities.
- Data Encryption: Encrypt sensitive data both at rest and in transit to protect it from unauthorized access. Encryption ensures that even if data is intercepted, it cannot be read without the appropriate decryption key.
- Secure Network Connections: Use secure protocols like HTTPS for communication between your cloud servers and clients. HTTPS encrypts data transmitted over the internet, making it more difficult for attackers to eavesdrop on communication.
Role of Cloud Security Services and Compliance Regulations
Cloud providers offer a range of security services to help organizations secure their cloud environments. These services can include:
- Security Information and Event Management (SIEM): SIEM solutions collect and analyze security data from various sources to detect and respond to security threats.
- Vulnerability Scanning: Vulnerability scanning tools identify security weaknesses in cloud infrastructure and applications.
- Data Loss Prevention (DLP): DLP solutions help organizations prevent sensitive data from leaving their cloud environments without authorization.
- Security Monitoring and Incident Response: Cloud providers offer 24/7 security monitoring and incident response services to detect and respond to security incidents quickly.
Compliance regulations, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA), also play a significant role in cloud security. These regulations set standards for data protection, privacy, and security, requiring organizations to implement appropriate security measures to comply with the law.
Cloud Web Server Hosting for Specific Use Cases
Cloud web server hosting offers a flexible and scalable solution that can cater to a wide range of use cases. From e-commerce platforms to content-heavy websites, cloud hosting can provide the necessary resources and features to ensure optimal performance and reliability.
E-commerce
E-commerce businesses heavily rely on their websites for sales and customer engagement. Cloud hosting can significantly benefit e-commerce platforms by providing:
- Scalability: Cloud hosting allows e-commerce businesses to easily scale their resources up or down based on traffic fluctuations, ensuring a smooth shopping experience even during peak seasons or promotional events.
- High Availability: Cloud hosting providers offer redundancy and failover mechanisms, ensuring that the e-commerce website remains accessible even in case of server failures or outages. This is crucial for maintaining customer trust and avoiding revenue loss.
- Security: Cloud hosting providers invest heavily in security measures, offering robust firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and regular security updates. This helps e-commerce businesses protect sensitive customer data and comply with industry regulations.
Blogging
Bloggers and content creators often require reliable hosting solutions that can handle fluctuating traffic and ensure fast loading times. Cloud hosting offers several advantages for blogging:
- Cost-Effectiveness: Cloud hosting allows bloggers to pay only for the resources they use, making it a cost-effective option compared to dedicated servers, especially for smaller blogs with moderate traffic.
- Performance Optimization: Cloud hosting provides access to powerful servers and advanced caching mechanisms, ensuring fast loading times for blog posts and improving user experience.
- Content Delivery Networks (CDNs): Cloud hosting providers often integrate with CDNs, which distribute website content across multiple servers globally. This reduces latency and improves website speed for users worldwide.
Development
Software development teams require environments that are flexible, scalable, and secure to support their projects. Cloud hosting offers several advantages for development teams:
- Rapid Deployment: Cloud hosting allows developers to quickly deploy and test applications in a secure and isolated environment. This accelerates the development process and reduces time to market.
- Collaboration: Cloud hosting provides tools and platforms for collaboration, allowing developers to work together on projects from different locations. This improves team productivity and facilitates seamless communication.
- DevOps Integration: Cloud hosting seamlessly integrates with DevOps tools and workflows, automating tasks such as deployment, monitoring, and scaling. This streamlines the development process and enhances efficiency.
Industries and Businesses
Cloud web server hosting has become increasingly popular across various industries and businesses, offering numerous benefits:
- Financial Services: Cloud hosting enables financial institutions to provide secure and reliable online banking services, ensuring data privacy and compliance with regulations.
- Healthcare: Cloud hosting supports the storage and processing of sensitive patient data, ensuring compliance with HIPAA regulations and providing secure access for healthcare professionals.
- Education: Cloud hosting allows educational institutions to provide online learning platforms, virtual classrooms, and digital content libraries, enhancing accessibility and flexibility for students.
- Retail: Cloud hosting empowers retailers to create online stores, manage inventory, and process orders efficiently, providing a seamless shopping experience for customers.
Business Objectives
Cloud hosting can be used to support specific business objectives, including:
- Disaster Recovery: Cloud hosting providers offer disaster recovery services, ensuring that businesses can quickly recover from data loss or system failures. This minimizes downtime and reduces the impact of disruptions on business operations.
- Global Reach: Cloud hosting enables businesses to expand their reach to international markets by providing low-latency access to users worldwide. This can be achieved through CDNs and geographically distributed data centers.
- Cost Optimization: Cloud hosting allows businesses to pay only for the resources they use, reducing infrastructure costs and optimizing IT budgets. This is especially beneficial for businesses with fluctuating workloads or seasonal demands.
Wrap-Up: Cloud Web Server Hosting
As the digital world continues to evolve, cloud web server hosting remains a vital cornerstone for businesses seeking to optimize their online presence. By embracing the advantages of scalability, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness, cloud hosting empowers organizations to navigate the dynamic landscape of the internet with confidence. From small startups to large enterprises, cloud web server hosting provides the foundation for a future-proof online strategy, enabling businesses to achieve their digital goals with ease and efficiency.