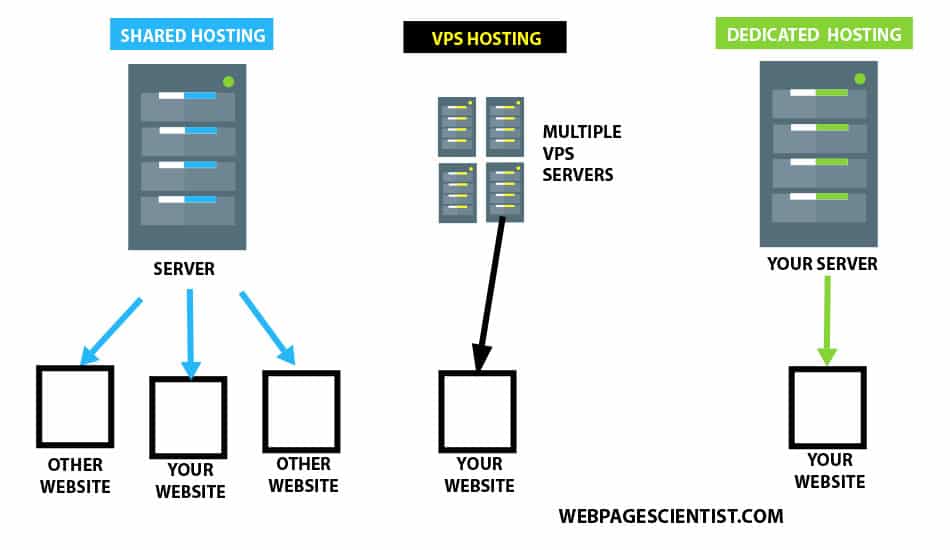
Cheap MySQL hosting can be a tempting option, especially for those starting out or on a tight budget. But is it really the best choice for your website? The term “cheap” can be subjective, and it’s important to understand what you’re getting for your money. This guide will delve into the world of cheap MySQL hosting, exploring the different types, key factors to consider, and how to choose the right provider for your specific needs.
We’ll examine the features and functionalities of cheap MySQL hosting packages, discuss the pros and cons of different hosting types like shared, VPS, and cloud, and highlight the importance of uptime, reliability, data security, and customer support. Additionally, we’ll provide practical tips for optimizing your MySQL database performance and minimizing hosting costs while ensuring your website remains fast and secure.
Budgeting and Cost Considerations
When choosing cheap MySQL hosting, it’s essential to understand the cost factors involved and how to optimize your budget while maintaining performance. While low prices are attractive, it’s crucial to consider the overall value and potential hidden costs.
Common Cost Factors
Understanding the typical cost factors associated with cheap MySQL hosting can help you make informed decisions and avoid surprises. These factors often influence the overall price:
- Monthly Fees: This is the recurring cost for using the hosting service, typically billed monthly. The price can vary significantly depending on the resources offered, such as storage space, bandwidth, and database features.
- Storage: The amount of disk space allocated for your website files, database, and other data. More storage usually translates to higher monthly fees.
- Bandwidth: The amount of data transferred between your website and visitors. High traffic websites require more bandwidth, which can increase costs.
- Database Features: Some hosting providers offer advanced database features like replication, backups, and performance optimization tools. These features may come with additional costs.
Minimizing Hosting Costs
Several strategies can help you minimize hosting costs while maintaining performance:
- Choose a Hosting Plan that Fits Your Needs: Opt for a plan that provides sufficient resources without overspending. If your website has low traffic, a basic plan might suffice. However, if you expect significant growth, consider a plan with more resources.
- Optimize Your Website for Performance: A well-optimized website requires fewer resources, potentially reducing your hosting costs. This includes optimizing images, minimizing HTTP requests, and using caching techniques.
- Monitor and Manage Your Resources: Regularly monitor your website’s resource usage (storage, bandwidth, database queries) to identify potential areas for optimization and cost reduction.
- Consider Cloud Hosting: Cloud hosting offers flexibility and scalability, allowing you to pay only for the resources you use. This can be cost-effective, especially for websites with fluctuating traffic patterns.
Optimizing MySQL Database Performance
Optimizing your MySQL database can significantly improve performance and potentially reduce hosting costs. Here are some key strategies:
- Database Indexing: Indexing allows for faster data retrieval, improving query performance. Create indexes on frequently queried columns to speed up searches.
- Query Optimization: Analyze your queries and identify areas for improvement. Use appropriate SQL syntax, optimize table joins, and avoid unnecessary operations.
- Database Caching: Cache frequently accessed data to reduce database load and improve response times. This can be done using tools like Memcached or Redis.
- Database Tuning: Adjust database configuration parameters like buffer pool size, query cache size, and thread count to optimize performance based on your website’s specific needs.
Alternatives to Cheap MySQL Hosting
While cheap MySQL hosting can be a budget-friendly option for smaller websites and projects, it may not always be the best choice for larger or more demanding applications. Exploring alternative solutions can lead to greater performance, scalability, and control over your database environment.
Self-Hosting MySQL, Cheap mysql hosting
Self-hosting MySQL provides complete control over your database environment, allowing for customization and fine-tuning to meet specific needs. However, it also involves greater responsibility for maintenance, security, and resource management.
Advantages of Self-Hosting MySQL
- Complete Control: Self-hosting gives you full control over the database server, including configuration, updates, and backups.
- Customization: You can customize the database environment to match your specific requirements, such as performance optimization and security settings.
- Cost-Effective: In the long run, self-hosting can be more cost-effective than relying on a paid hosting provider, especially for large or demanding applications.
Disadvantages of Self-Hosting MySQL
- Technical Expertise: Self-hosting requires technical expertise in server administration, database management, and security.
- Maintenance: You are responsible for all maintenance tasks, including updates, backups, and security patching.
- Resource Management: You need to manage server resources, such as CPU, memory, and storage, to ensure optimal performance.
Alternative Database Management Systems
Beyond MySQL, several other database management systems (DBMS) offer distinct advantages and disadvantages, catering to different needs.
PostgreSQL
PostgreSQL is an open-source object-relational database system known for its reliability, data integrity, and advanced features.
Advantages of PostgreSQL
- Data Integrity: PostgreSQL is known for its strong data integrity features, ensuring data consistency and accuracy.
- Advanced Features: It offers advanced features such as stored procedures, triggers, and foreign key constraints.
- Open Source: Being open source, PostgreSQL is free to use and offers a large community for support and development.
Disadvantages of PostgreSQL
- Performance: PostgreSQL can be slower than MySQL for certain workloads, especially those involving high write operations.
- Complexity: PostgreSQL has a more complex syntax and feature set compared to MySQL, requiring a steeper learning curve.
MongoDB
MongoDB is a NoSQL database that uses a document-oriented data model, making it well-suited for handling unstructured data and scaling horizontally.
Advantages of MongoDB
- Scalability: MongoDB is designed for horizontal scalability, allowing you to easily add more servers as your data grows.
- Flexibility: Its document-oriented model provides flexibility in handling unstructured data, such as JSON objects.
- Performance: MongoDB can be very fast for read operations, making it suitable for applications with high read volumes.
Disadvantages of MongoDB
- Data Integrity: MongoDB’s schema-less design can lead to data inconsistencies if not carefully managed.
- SQL Support: MongoDB does not fully support SQL queries, requiring a different approach to data retrieval.
Comparing Costs and Features
| DBMS | Cost | Features | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MySQL | Free (Open Source) or Paid Hosting | Relational Database, SQL Support, High Performance | Widely Used, Mature Technology, Excellent Performance for Read Operations | Limited Scalability, Less Robust Data Integrity Compared to PostgreSQL |
| PostgreSQL | Free (Open Source) | Relational Database, SQL Support, Advanced Features, Strong Data Integrity | Reliable, Data Integrity, Advanced Features, Open Source | Performance Can Be Slower for Write Operations, More Complex |
| MongoDB | Free (Open Source) or Paid Hosting | NoSQL Database, Document-Oriented Model, High Scalability | Scalability, Flexibility for Unstructured Data, Fast Read Operations | Data Integrity Challenges, SQL Support Limitations |
Final Conclusion
In the realm of cheap MySQL hosting, finding the right balance between affordability and performance is crucial. While cost-effective solutions can be attractive, remember that reliability, security, and scalability are equally important. By carefully evaluating your needs, researching reputable providers, and implementing best practices, you can choose a hosting plan that meets your requirements without compromising on quality. Remember, ongoing monitoring and maintenance are essential for optimal performance and long-term success.