VPS dedicated server sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail and brimming with originality from the outset.
VPS dedicated servers represent a compelling solution for those seeking a balance between shared hosting’s affordability and the robust control and resources of a dedicated server. This guide delves into the intricacies of VPS dedicated servers, providing a comprehensive understanding of their features, advantages, and use cases. We’ll explore how VPS dedicated servers empower businesses and individuals to manage their online presence with greater autonomy and performance.
VPS vs. Dedicated Server
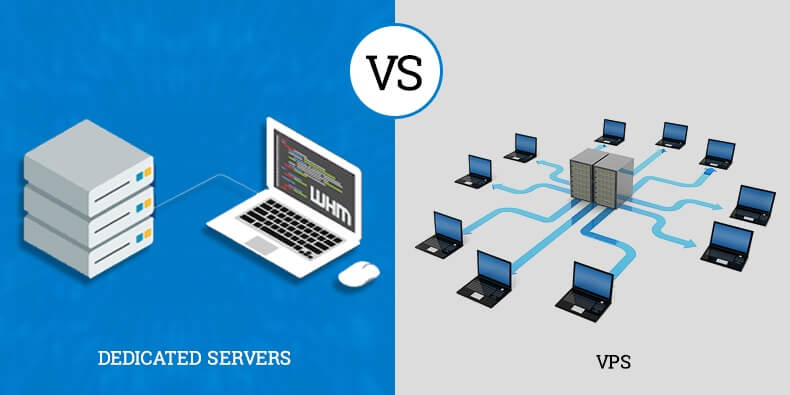
Choosing the right server infrastructure for your website or application can be a daunting task. Two popular options often considered are Virtual Private Servers (VPS) and Dedicated Servers. Understanding the fundamental differences between these two server types is crucial for making an informed decision.
VPS vs. Dedicated Server: Key Differences
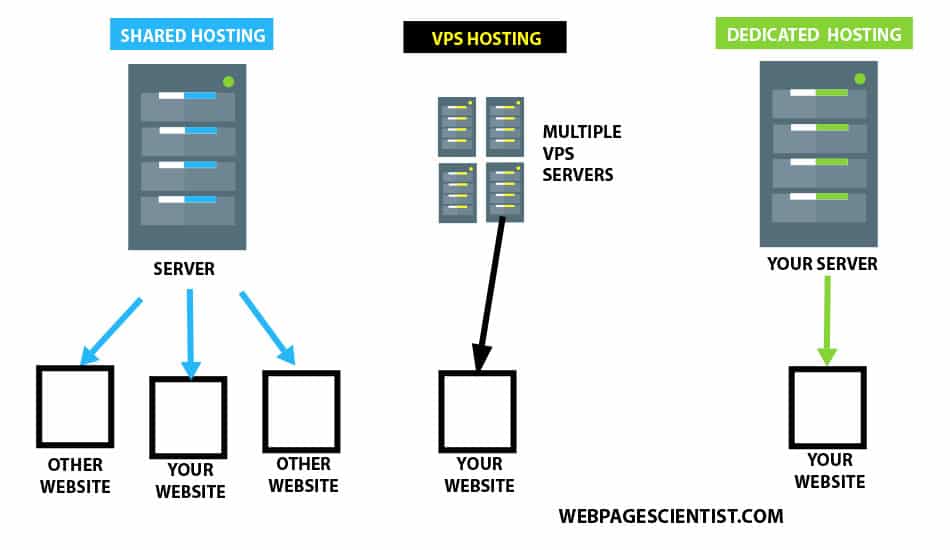
VPS and Dedicated Servers are distinct server types that cater to different needs and offer varying levels of resources and control. A VPS is a virtualized server environment where a single physical server is partitioned into multiple virtual servers. Each VPS operates independently, offering a degree of isolation and resources, but sharing the underlying physical hardware with other virtual servers. Conversely, a Dedicated Server provides exclusive access to a physical server, offering complete control over the hardware and software configuration.
Performance and Resources
VPS servers offer a balance between performance and affordability. They provide more resources than shared hosting environments but are less powerful than Dedicated Servers. The performance of a VPS is influenced by factors like the number of virtual servers on the physical server, the allocated resources, and the underlying hardware specifications. Dedicated Servers, on the other hand, deliver superior performance as they offer dedicated access to the server’s resources. This means no resource contention with other users, leading to consistent performance and responsiveness.
Control and Customization
VPS servers offer a moderate level of control over the server environment. Users can typically install their preferred operating system and software, but they might have limited access to the underlying hardware. Dedicated Servers provide the highest level of control, allowing users to configure the hardware, install any software, and manage the server environment according to their specific requirements.
Pros and Cons of VPS and Dedicated Servers
VPS and Dedicated Servers have their own advantages and disadvantages.
VPS Pros:
- Cost-Effective: VPS servers are typically more affordable than Dedicated Servers, making them a budget-friendly option for businesses and individuals with moderate resource requirements.
- Scalability: VPS servers offer a degree of scalability, allowing users to upgrade their resources as their needs evolve. This flexibility can be beneficial for businesses experiencing growth.
- Ease of Management: Many VPS providers offer user-friendly control panels and management tools, simplifying server administration tasks.
VPS Cons:
- Shared Resources: VPS servers share the underlying physical hardware with other virtual servers, which can lead to performance fluctuations if other users experience heavy resource demands.
- Limited Control: Users have limited control over the underlying hardware and might face restrictions on certain configurations.
- Security Concerns: Sharing the physical hardware with other users can potentially expose the VPS server to security risks.
Dedicated Server Pros:
- Unmatched Performance: Dedicated Servers offer the highest level of performance as they provide exclusive access to the server’s resources.
- Complete Control: Users have full control over the hardware and software configuration, enabling them to tailor the server environment to their specific needs.
- Enhanced Security: Dedicated Servers provide a secure environment as they are not shared with other users, reducing the risk of security breaches.
Dedicated Server Cons:
- Higher Cost: Dedicated Servers are significantly more expensive than VPS servers, making them a less budget-friendly option.
- Technical Expertise Required: Managing a Dedicated Server requires a higher level of technical expertise, as users are responsible for all aspects of server administration.
- Limited Scalability: Scaling up a Dedicated Server can be more complex and expensive compared to VPS servers.
Real-World Examples
Here are some real-world examples of scenarios where a VPS or a Dedicated Server might be more suitable:
VPS:
- Small Businesses: A VPS can be a cost-effective solution for small businesses with moderate website traffic and resource requirements.
- Blogs and Personal Websites: For blogs and personal websites with moderate traffic, a VPS can provide a reliable and scalable platform.
- Development and Testing Environments: VPS servers are often used for development and testing environments, offering a controlled and isolated environment for software development.
Dedicated Server:
- High-Traffic Websites: Dedicated Servers are ideal for high-traffic websites and applications that require consistent performance and high availability.
- E-commerce Platforms: For online stores with large databases and complex functionalities, a Dedicated Server can provide the necessary resources and security.
- Gaming Servers: Dedicated Servers are often used for gaming servers, providing low latency and dedicated resources for a smooth gaming experience.
VPS Features and Capabilities
Virtual Private Servers (VPS) offer a robust and flexible hosting solution that bridges the gap between shared hosting and dedicated servers. VPS technology provides a virtualized environment on a physical server, allowing users to enjoy enhanced performance, security, and control compared to shared hosting.
VPS Features
VPS solutions offer a range of features designed to enhance performance, security, and manageability. These features include:
- Dedicated Resources: VPSs allocate dedicated resources like CPU, RAM, and storage to each user, ensuring predictable performance and avoiding resource contention issues common in shared hosting environments.
- Root Access: VPS users typically have root access to their server, granting them full control over the operating system, software installations, and configurations. This allows for customization and optimization to meet specific needs.
- Multiple Operating Systems: VPS providers often support a variety of operating systems (OS), including Linux distributions like CentOS, Ubuntu, and Debian, and Windows Server. This flexibility allows users to choose the OS best suited for their applications and preferences.
- Scalability: VPS solutions offer scalability, enabling users to easily upgrade their resources as their needs grow. This allows for seamless expansion without the need to migrate to a new server.
- Isolation: VPSs provide isolation between users, preventing interference and ensuring that one user’s actions do not impact others on the same physical server. This enhances security and stability.
- Control Panel: Many VPS providers offer user-friendly control panels, simplifying server management tasks such as resource allocation, security updates, and software installations.
Benefits of Using a VPS
VPS hosting offers several benefits over shared hosting, making it a popular choice for various applications:
- Enhanced Performance: Dedicated resources and isolation guarantee predictable performance, minimizing the impact of other users on the server. This results in faster loading times, improved application responsiveness, and a smoother user experience.
- Increased Security: Root access and control over the server environment allow users to implement robust security measures, including firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and regular security updates. This minimizes the risk of security breaches and data loss.
- Flexibility and Customization: Root access empowers users to install and configure software, customize server settings, and optimize performance to meet specific requirements. This flexibility is essential for web development, application deployment, and running specialized applications.
- Cost-Effectiveness: While VPS hosting is more expensive than shared hosting, it offers a cost-effective alternative to dedicated servers. Users can enjoy the benefits of a dedicated environment at a fraction of the cost.
Impact of VPS Features on Performance, Security, and Scalability
The features of a VPS significantly impact its performance, security, and scalability. Here’s a table summarizing the impact of key features:
| Feature | Impact on Performance | Impact on Security | Impact on Scalability |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dedicated Resources | Increased performance due to dedicated CPU, RAM, and storage. | No impact on security directly, but it enables better resource allocation for security measures. | Enables easy scaling by adding more resources as needed. |
| Root Access | Improved performance through customization and optimization. | Enhanced security through customization of security measures. | Allows for flexible scaling and customization of resources. |
| Multiple Operating Systems | No direct impact on performance, but allows for choosing the most efficient OS for the application. | No direct impact on security, but choosing a secure OS is important. | No direct impact on scalability, but allows for choosing an OS that supports future scaling needs. |
| Scalability | Allows for easy scaling of resources to meet performance demands. | No direct impact on security, but ensures sufficient resources for security measures as the server grows. | Enables seamless scaling of resources as the workload increases. |
| Isolation | Minimizes performance impact from other users. | Enhanced security by preventing interference from other users. | No direct impact on scalability, but ensures a stable environment for scaling. |
| Control Panel | Simplified server management, leading to better performance. | Easier management of security updates and configurations. | Streamlined resource management for efficient scaling. |
Choosing the Right VPS
Selecting the ideal VPS for your needs can be a complex process. Many factors, from performance to pricing, influence the decision. This guide provides a step-by-step approach to help you choose the best VPS for your specific requirements.
Factors to Consider
- CPU: The processing power of the VPS, measured in cores and clock speed. Higher core counts and faster clock speeds improve performance for resource-intensive tasks, such as running multiple applications or handling high traffic volumes.
- RAM: The amount of memory available for your VPS to store data and run applications. More RAM is essential for applications requiring large amounts of data, such as databases or web servers with high traffic.
- Storage: The type and size of storage provided by the VPS. Options include SSDs (Solid State Drives), HDDs (Hard Disk Drives), and NVMe drives. SSDs offer faster read/write speeds compared to HDDs, while NVMe drives provide the highest performance. Storage capacity should be sufficient for your data and application needs.
- Bandwidth: The amount of data that can be transferred in and out of your VPS. Higher bandwidth is crucial for applications requiring high data transfer rates, such as streaming services or large file downloads.
- Operating System: The software platform that runs on your VPS. Popular choices include Linux distributions like Ubuntu, CentOS, and Debian, as well as Windows Server. Choose an operating system compatible with your applications and development environment.
Essential Features Checklist
- Scalability: The ability to easily upgrade your VPS resources as your needs grow. Look for providers offering flexible scaling options.
- Security: Robust security features, including firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and regular security updates. Consider providers offering managed security services.
- Support: Reliable customer support, including 24/7 availability and multiple support channels. Look for providers offering responsive and knowledgeable support.
- Monitoring: Tools for monitoring your VPS performance and resource usage. Consider providers offering built-in monitoring features or integration with third-party monitoring tools.
- Backups: Regular backups of your VPS data to protect against data loss. Choose providers offering automatic backups or options for manual backups.
VPS Pricing Models
- Pay-as-you-go: You pay for the resources you use. This model is ideal for short-term projects or when you need to scale resources up and down frequently.
- Fixed monthly fee: You pay a fixed amount each month for a specific set of resources. This model is suitable for long-term projects with predictable resource needs.
- Bundled packages: Providers offer pre-configured VPS packages with specific resource allocations and pricing. This model can be convenient for users who need a specific set of resources.
Choosing the Right VPS Provider
- Research and compare: Explore different VPS providers and compare their features, pricing, and customer reviews.
- Consider your needs: Identify your specific resource requirements, such as CPU, RAM, storage, and bandwidth.
- Evaluate the provider’s reputation: Check the provider’s track record, uptime, and customer support.
- Choose a provider that aligns with your budget: Select a pricing model and package that fits your budget and resource needs.
VPS Hosting Providers
Choosing the right VPS hosting provider is crucial for ensuring optimal performance, reliability, and security for your website or application. Several reputable providers offer a range of VPS hosting plans to suit different needs and budgets.
Reputable VPS Hosting Providers
This section provides a list of well-established and reputable VPS hosting providers, along with their key features, pricing, and customer support options.
- DigitalOcean: Known for its user-friendly interface, extensive documentation, and affordable pricing. DigitalOcean offers a variety of VPS plans with different RAM, storage, and CPU configurations, starting at $5 per month. They provide excellent customer support through their documentation, community forums, and live chat.
- Linode: A popular choice for developers and businesses seeking high-performance VPS hosting. Linode offers a wide range of VPS plans with flexible configurations and competitive pricing. They also provide a comprehensive API for automation and a dedicated support team available 24/7.
- Vultr: Known for its fast server speeds, global server locations, and simple pricing structure. Vultr offers a variety of VPS plans with different RAM, storage, and CPU configurations, starting at $2.50 per month. They provide a user-friendly control panel and excellent customer support through their knowledge base and ticketing system.
- AWS (Amazon Web Services): A leading cloud computing provider offering a wide range of VPS hosting solutions, including EC2 instances. AWS provides a vast array of features, such as scalability, security, and advanced networking options. Their pricing is based on usage, and they offer a free tier for new users.
- Google Cloud Platform: Another major cloud provider offering powerful VPS hosting solutions, including Compute Engine instances. Google Cloud Platform provides high-performance computing resources, global infrastructure, and advanced features like machine learning and AI. Their pricing is based on usage, and they offer a free tier for new users.
Comparing VPS Hosting Providers
This section presents a table comparing the strengths and weaknesses of different VPS hosting providers. This information can help you make an informed decision based on your specific requirements.
| Provider | Strengths | Weaknesses |
|---|---|---|
| DigitalOcean | User-friendly interface, extensive documentation, affordable pricing | Limited customization options for advanced users |
| Linode | High-performance servers, comprehensive API, 24/7 support | Pricing can be higher than some competitors |
| Vultr | Fast server speeds, global server locations, simple pricing | Limited features compared to some cloud providers |
| AWS | Vast array of features, scalability, advanced networking options | Complex pricing structure, steep learning curve |
| Google Cloud Platform | High-performance computing resources, global infrastructure, advanced features | Complex pricing structure, steep learning curve |
Researching Provider Reputation and Customer Reviews
Before making a decision, it is essential to research the reputation and customer reviews of potential VPS hosting providers. This can provide valuable insights into their reliability, performance, and customer support quality.
- Read online reviews: Websites like Trustpilot, G2, and Sitejabber offer independent customer reviews that can help you gauge a provider’s reputation.
- Check forum discussions: Online forums dedicated to web hosting can provide insights into user experiences with different VPS hosting providers.
- Look for industry awards and recognition: Awards and recognition from reputable organizations can indicate a provider’s commitment to quality and customer satisfaction.
“It’s crucial to understand that choosing the right VPS hosting provider is a significant decision that can impact your website’s performance, reliability, and security. Thorough research and due diligence are essential to ensure you select a provider that meets your specific needs and budget.”
VPS Security and Management
A VPS, while offering more control than shared hosting, requires you to take responsibility for its security. Implementing robust security measures is crucial to protect your data and prevent unauthorized access. This section will discuss essential security practices for your VPS, covering topics such as firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and regular security updates. We’ll also explore best practices for managing and monitoring your VPS environment, including server configuration, software updates, and troubleshooting common issues.
Firewall Configuration
Firewalls act as a barrier between your VPS and the external world, blocking unauthorized access attempts. They analyze incoming and outgoing network traffic, allowing only authorized connections.
- Enable the Built-in Firewall: Most VPS providers offer a built-in firewall, which should be enabled by default. However, it’s essential to verify its status and ensure it’s configured correctly.
- Configure Firewall Rules: Create specific rules to allow access to essential ports and services, such as SSH for remote management, HTTP for your website, and FTP for file transfers. Block all other ports to enhance security.
- Use a Hardware Firewall: For an additional layer of protection, consider using a hardware firewall. This device sits between your VPS and the internet, providing a more robust security barrier.
Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS)
Intrusion detection systems (IDS) monitor your VPS for suspicious activities and alert you to potential threats. They analyze network traffic and system logs, identifying patterns that could indicate malicious activity.
- Software-based IDS: Several open-source and commercial IDS solutions are available, such as Snort, Suricata, and AIDE. These solutions can be installed and configured on your VPS to monitor for suspicious activity.
- Cloud-based IDS: Some cloud providers offer managed IDS services that can monitor your VPS and provide real-time threat detection and alerts.
- Real-time Monitoring: Configure your IDS to send alerts in real-time, allowing you to respond quickly to potential threats. This can help prevent data breaches and minimize damage.
Regular Security Updates
Keeping your VPS software up-to-date is crucial for security. Software updates often include security patches that fix vulnerabilities exploited by attackers.
- Operating System Updates: Regularly update your VPS operating system to patch vulnerabilities and improve security. Most distributions offer automatic updates, but it’s good practice to manually check for updates periodically.
- Application Updates: Update all applications installed on your VPS, including web servers, databases, and other software. Ensure that your applications are always running the latest versions.
- Security Patch Management: Implement a process for managing security patches, including testing updates in a staging environment before deploying them to your live server.
Best Practices for Managing and Monitoring a VPS
Effective VPS management involves implementing best practices to ensure security and stability.
- Regular Backups: Create regular backups of your VPS data to protect against data loss due to hardware failure, software errors, or malicious attacks. Store backups in a secure location, preferably off-site.
- Strong Passwords and Two-Factor Authentication: Use strong, unique passwords for all accounts on your VPS, including SSH, web server, and database accounts. Enable two-factor authentication for added security.
- Monitor System Logs: Regularly review your VPS system logs for any suspicious activity or error messages. This can help identify potential security threats or performance issues.
- Restrict User Access: Limit user access to only the necessary files and directories. Use the principle of least privilege, granting users only the permissions they need to perform their tasks.
- Regular Security Audits: Conduct regular security audits to assess your VPS’s security posture and identify any weaknesses or vulnerabilities. This can be done manually or using automated tools.
Server Configuration
Properly configuring your VPS server settings is crucial for security and performance.
- Secure SSH Access: Use a strong SSH password and enable SSH key-based authentication to secure remote access to your VPS. Disable root login and use a dedicated user account for management tasks.
- Disable Unnecessary Services: Disable any services or applications that are not required for your VPS’s functionality. This reduces the attack surface and minimizes security risks.
- Optimize Security Settings: Configure your web server, database, and other applications with appropriate security settings, such as disabling file uploads, limiting access to specific directories, and enabling security headers.
Software Updates
Keeping your VPS software up-to-date is crucial for security and performance. Software updates often include security patches that fix vulnerabilities exploited by attackers.
- Automatic Updates: Enable automatic updates for your operating system and applications to ensure that you’re always running the latest versions.
- Manual Updates: Regularly check for updates manually and install them promptly. You can use the `apt-get update` and `apt-get upgrade` commands on Debian-based systems or `yum update` on Red Hat-based systems to update your system.
- Test Updates: Before applying updates to your live server, test them in a staging environment to ensure that they don’t cause any compatibility issues or performance problems.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Troubleshooting common VPS issues is an essential part of managing your server.
- Performance Issues: Monitor your VPS’s performance using tools like `top`, `htop`, and `iostat`. Identify bottlenecks and optimize resource usage.
- Network Connectivity Issues: Check your network configuration, including IP addresses, DNS settings, and firewall rules. Use tools like `ping` and `traceroute` to diagnose connectivity problems.
- Security Incidents: Investigate suspicious activity, including unusual login attempts, unauthorized file access, or unexpected system behavior. Take appropriate steps to mitigate the threat and restore security.
VPS Applications and Use Cases

VPS servers are versatile and adaptable, catering to a wide range of applications across diverse industries. Their scalability, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness make them an ideal choice for businesses and individuals alike.
VPS servers offer a compelling alternative to shared hosting, providing users with dedicated resources and greater control over their environment. Let’s explore the various applications and use cases where VPS shines.
Web Hosting
VPS hosting is a popular choice for websites with moderate to high traffic volumes. Unlike shared hosting, where multiple websites share the same server resources, VPS provides dedicated resources, ensuring better performance and reliability.
VPS servers offer enhanced security, as users have root access to their virtual machine, allowing them to install and configure security measures tailored to their specific needs.
VPS hosting is also ideal for websites with resource-intensive applications, such as e-commerce platforms, content management systems (CMS), and online gaming platforms.
E-commerce
VPS servers are an excellent choice for businesses running e-commerce websites. They provide the necessary resources to handle high traffic volumes, secure online transactions, and store large amounts of data.
VPS servers also offer greater flexibility, allowing businesses to scale their resources up or down as needed to meet changing demands.
Gaming Servers
VPS servers are widely used for hosting online gaming servers. They provide dedicated resources, low latency, and high bandwidth, ensuring a smooth and enjoyable gaming experience for players.
VPS servers offer greater control over server settings, allowing game administrators to customize the gaming environment to their liking.
VPS servers also provide enhanced security, protecting game servers from attacks and ensuring the integrity of the gaming environment.
Software Development
VPS servers are invaluable tools for software developers. They provide a stable and secure environment for developing, testing, and deploying applications.
VPS servers offer flexibility, allowing developers to choose the operating system and software packages that best suit their needs.
VPS servers also provide greater control over the development environment, enabling developers to fine-tune settings and optimize performance.
Case Studies
Many businesses and individuals have successfully implemented VPS solutions. For example, a small startup using VPS servers for their e-commerce website experienced significant performance improvements and increased sales.
A popular online gaming community adopted VPS servers to host their game servers, resulting in reduced latency and a more enjoyable gaming experience for their players.
A software development team leveraging VPS servers for their development environment reported increased productivity and efficiency.
Emerging Trends and Future Possibilities
The future of VPS technology is bright. With the increasing demand for cloud computing, VPS servers are expected to play a significant role in the future of web hosting, software development, and other applications.
Emerging trends, such as the rise of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML), are driving the need for more powerful and scalable computing resources, making VPS servers an even more attractive option.
The integration of VPS technology with other cloud-based services, such as serverless computing and edge computing, is expected to further enhance the capabilities and applications of VPS servers.
VPS Scalability and Performance Optimization
VPS scalability and performance optimization are crucial aspects of ensuring a smooth and efficient user experience. A well-optimized VPS can handle growing demands, deliver fast loading times, and minimize downtime.
Adjusting Resources and Configurations
Scaling your VPS resources allows you to adapt to changing traffic patterns and workload requirements. When your VPS starts experiencing performance issues due to increased traffic or resource-intensive applications, you can adjust your configuration by:
– Upgrading your plan: Consider upgrading to a VPS plan with more RAM, CPU cores, or storage space. This provides the necessary resources to handle the increased workload.
– Adding more RAM: If your applications are memory-intensive, increasing RAM can significantly improve performance.
– Increasing CPU cores: For CPU-bound tasks, adding more CPU cores can speed up processing and improve responsiveness.
– Expanding storage space: If your storage is running low, expanding it can prevent performance bottlenecks and ensure enough space for your data and applications.
Improving VPS Performance
Several techniques can enhance your VPS’s performance, ensuring optimal speed and responsiveness. These include:
– Caching: Caching frequently accessed data in memory can reduce database queries and improve website loading times.
– Optimization: Optimizing your website code, database queries, and images can significantly improve loading speeds.
– Load balancing: Distributing traffic across multiple servers can reduce the load on a single VPS, improving performance and reliability.
– Regular maintenance: Keeping your VPS software and operating system up to date with the latest security patches and updates can prevent performance issues and security vulnerabilities.
– Monitoring and analysis: Regularly monitoring your VPS performance metrics like CPU usage, RAM consumption, and disk space can help identify potential bottlenecks and proactively address them.
Common Performance Bottlenecks and Solutions
| Bottleneck | Solution |
|---|---|
| High CPU usage | Upgrade to a VPS plan with more CPU cores or optimize your applications to reduce CPU-intensive operations. |
| Low RAM availability | Increase RAM allocation or optimize your applications to reduce memory consumption. |
| Slow disk I/O | Upgrade to a VPS plan with faster storage or use caching techniques to reduce disk access. |
| Network congestion | Consider a VPS provider with a robust network infrastructure or use load balancing to distribute traffic across multiple servers. |
VPS vs. Cloud Hosting
VPS and cloud hosting are popular choices for businesses and individuals looking for more powerful and flexible hosting solutions than shared hosting. Both options offer distinct advantages and disadvantages, making it crucial to understand their differences to choose the best fit for your specific needs.
Comparing VPS and Cloud Hosting
VPS and cloud hosting share some similarities, such as providing dedicated resources and greater control than shared hosting. However, they differ significantly in their architecture, scalability, and pricing models.
- VPS: Virtual Private Server (VPS) creates a virtual environment on a physical server, dividing its resources among multiple users. Each VPS has its own operating system, software, and dedicated resources, ensuring isolation and better performance than shared hosting.
- Cloud Hosting: Cloud hosting utilizes a network of interconnected servers to distribute resources and applications. Instead of a single physical server, data and applications are spread across multiple servers, ensuring high availability and scalability.
Advantages and Disadvantages of VPS and Cloud Hosting
Both VPS and cloud hosting offer unique advantages and disadvantages, influencing their suitability for specific use cases.
VPS Advantages
- Cost-effectiveness: VPS hosting is generally more affordable than cloud hosting, especially for smaller websites and applications with consistent resource requirements.
- Dedicated Resources: VPS provides dedicated resources, ensuring consistent performance and predictable resource allocation, even during peak traffic periods.
- Root Access and Control: VPS users have root access and complete control over their virtual server, allowing for greater customization and flexibility in managing their environment.
VPS Disadvantages
- Limited Scalability: Scaling a VPS requires upgrading to a larger server or adding more servers, which can be time-consuming and disruptive.
- Single Point of Failure: If the physical server hosting the VPS fails, the entire VPS becomes unavailable, leading to potential downtime.
- Limited Flexibility: VPS resources are allocated at the time of purchase and may not be easily adjusted to meet fluctuating demands.
Cloud Hosting Advantages
- Scalability and Flexibility: Cloud hosting allows for easy scaling of resources on demand, automatically adjusting to fluctuating traffic and resource requirements.
- High Availability and Redundancy: Data and applications are distributed across multiple servers, ensuring high availability and redundancy in case of server failure.
- Pay-as-you-go Pricing: Cloud hosting providers typically offer pay-as-you-go pricing models, allowing users to pay only for the resources they consume, making it cost-effective for fluctuating workloads.
Cloud Hosting Disadvantages
- Higher Cost: Cloud hosting can be more expensive than VPS hosting, especially for consistent resource requirements.
- Limited Control: Cloud hosting providers typically manage the underlying infrastructure, offering less control over the server environment compared to VPS hosting.
- Security Concerns: Depending on the provider and configuration, cloud hosting can introduce security risks, requiring careful consideration of security measures and compliance.
Choosing the Right Hosting Option
The best choice between VPS and cloud hosting depends on several factors, including:
- Website Traffic and Resource Requirements: For websites with consistent traffic and predictable resource needs, VPS hosting can be a cost-effective solution. However, for websites with fluctuating traffic or high resource demands, cloud hosting offers better scalability and flexibility.
- Budget: VPS hosting is generally more affordable than cloud hosting, making it suitable for smaller businesses or projects with limited budgets. However, cloud hosting’s pay-as-you-go pricing can be more cost-effective for fluctuating workloads.
- Technical Expertise: VPS hosting requires more technical expertise, as users need to manage the server environment. Cloud hosting offers managed services, simplifying server management for users with limited technical skills.
- Scalability and Flexibility: For businesses anticipating rapid growth or fluctuating workloads, cloud hosting provides superior scalability and flexibility, allowing for seamless resource adjustments.
Real-world Examples of VPS and Cloud Hosting Use Cases
Businesses utilize both VPS and cloud hosting effectively, depending on their specific needs and requirements.
VPS Use Cases
- Small Businesses: Small businesses with consistent website traffic and limited budget often opt for VPS hosting to provide dedicated resources and cost-effective solutions.
- E-commerce Stores: E-commerce stores with moderate traffic and predictable resource demands often utilize VPS hosting for its reliable performance and cost-effectiveness.
- Gaming Servers: Dedicated gaming servers often utilize VPS hosting for its consistent performance and ability to handle high-intensity workloads.
Cloud Hosting Use Cases
- Large Enterprises: Large enterprises with fluctuating workloads and high resource demands often utilize cloud hosting for its scalability, flexibility, and high availability.
- Software Development: Cloud hosting provides a flexible and scalable platform for software development teams to host their applications and collaborate efficiently.
- Big Data Analytics: Cloud hosting offers powerful computing resources and storage capacity for handling large datasets and complex analytics tasks.
VPS vs. Shared Hosting
Choosing the right hosting solution for your website is crucial for its performance, security, and scalability. Two popular options are VPS (Virtual Private Server) and shared hosting. Understanding the key differences between these options will help you make an informed decision that aligns with your website’s needs.
Performance and Resources
VPS and shared hosting differ significantly in terms of performance and resources. Shared hosting involves sharing server resources with multiple websites on the same server. This means that your website’s performance can be affected by the activity of other websites on the server. VPS, on the other hand, provides a dedicated portion of a physical server, giving you more control over resources and ensuring better performance.
Advantages and Disadvantages
- Shared Hosting
- Advantages:
- Cost-effective: Shared hosting is typically the most affordable option, making it suitable for budget-conscious individuals or small websites with low traffic.
- Easy to use: Shared hosting platforms often offer user-friendly interfaces and automated setup processes, making it convenient for beginners.
- Disadvantages:
- Limited resources: Shared hosting offers limited resources, which can affect website performance, especially during peak traffic hours.
- Security risks: Sharing a server with multiple websites increases the risk of security breaches, as a compromised website can potentially affect others on the same server.
- Less control: Shared hosting provides limited control over server settings and configurations, which can be a disadvantage for websites with specific requirements.
- Advantages:
- VPS Hosting
- Advantages:
- Enhanced performance: VPS offers dedicated resources, resulting in improved website speed and responsiveness, even during high traffic periods.
- Increased security: VPS provides a more secure environment compared to shared hosting, as your website is isolated from other websites on the server.
- Greater control: VPS allows you to customize server settings and install software, providing greater flexibility and control over your website’s environment.
- Disadvantages:
- Higher cost: VPS hosting is generally more expensive than shared hosting due to the dedicated resources and increased control.
- Technical expertise required: Managing a VPS requires some technical knowledge and skills, as you are responsible for server maintenance and security.
- Advantages:
Resource Contention in Shared Hosting
Resource contention occurs when multiple websites on a shared server compete for the same resources, such as CPU, RAM, or bandwidth. This can lead to performance issues, such as slow loading times, website crashes, and increased latency. As the number of websites on a shared server increases, the competition for resources intensifies, potentially affecting the performance of all websites on the server.
VPS for Beginners

A Virtual Private Server (VPS) offers a great balance of affordability, control, and resources for individuals and businesses alike. However, managing a VPS can seem daunting for newcomers. This guide will equip you with the essential knowledge to navigate the world of VPS administration.
Understanding Essential Concepts
VPS administration involves several fundamental concepts that you need to grasp. These concepts provide the foundation for managing your VPS effectively.
- SSH Access: Secure Shell (SSH) is a secure protocol used to connect to your VPS remotely. It allows you to access and manage your server from your computer. SSH is crucial for executing commands, installing software, and managing files on your VPS.
- Command-Line Interface: The command-line interface (CLI) is a text-based environment where you interact with your VPS using commands. This interface is essential for performing various tasks, from installing software to configuring services.
- Server Configuration: Configuring your VPS involves customizing settings and parameters to optimize its performance and security. This includes managing software packages, setting up firewalls, and configuring network settings.
Setting Up Your VPS
Setting up a VPS involves a few initial steps to get your server ready for use. These steps are crucial for ensuring a smooth and secure setup.
- Choose a VPS Provider: Selecting a reliable VPS provider is the first step. Research providers based on factors like pricing, performance, customer support, and features. Popular providers include DigitalOcean, Linode, and Vultr.
- Create an Account and Choose a VPS Plan: Once you’ve chosen a provider, create an account and select a VPS plan that suits your needs. Consider factors like RAM, storage, and CPU cores when making your selection.
- Connect to Your VPS via SSH: After setting up your VPS, connect to it using SSH. You’ll need an SSH client like PuTTY (Windows) or Terminal (macOS/Linux). Your VPS provider will provide you with the necessary connection details.
- Install a Server Operating System: Your VPS provider will usually offer a selection of operating systems (OS) like Ubuntu, CentOS, or Debian. Choose an OS that aligns with your requirements and technical expertise.
- Configure Basic Security Settings: After installing your OS, configure basic security settings like setting strong passwords, enabling a firewall, and updating your system to the latest security patches.
Managing Your VPS
Managing your VPS involves various tasks that ensure its optimal performance and security. This includes routine maintenance, software updates, and security measures.
- Update Your System Regularly: Keeping your VPS updated with the latest security patches is essential to protect it from vulnerabilities and malware. Use the appropriate commands to update your system and installed packages.
- Monitor Server Performance: Regularly monitor your VPS’s performance using tools like htop or glances. This allows you to identify resource bottlenecks, potential issues, and optimize your server’s performance.
- Manage Disk Space: Regularly check your disk space usage and remove unnecessary files to prevent storage space depletion. Use tools like `df` to monitor your disk usage.
- Backup Your Data: Implement a regular data backup strategy to safeguard your data in case of hardware failures or accidental data loss. Utilize tools like rsync or dedicated backup services.
Common Challenges Faced by VPS Beginners
As a beginner, you might encounter certain challenges when managing your VPS. These challenges can be overcome with the right knowledge and resources.
- Understanding Command-Line Interface: The CLI can seem intimidating at first. Utilize online resources and tutorials to learn common commands and syntax. Practice using the CLI to become more comfortable.
- Troubleshooting Server Issues: Troubleshooting VPS issues can be challenging. Utilize error logs, search online forums, and consult with your VPS provider’s support team for assistance.
- Securing Your VPS: Ensuring your VPS is secure requires ongoing effort. Stay informed about security best practices, regularly update your system, and utilize security tools like firewalls and intrusion detection systems.
Resources and Tutorials for Learning More
Numerous resources and tutorials are available to help you learn more about VPS administration. These resources can provide valuable insights and practical guidance.
- VPS Provider Documentation: Most VPS providers offer comprehensive documentation and tutorials specific to their services. Utilize these resources to learn about their features, configurations, and troubleshooting tips.
- Online Forums and Communities: Engage with online forums and communities like Reddit (r/VPS) or ServerFault to ask questions, seek advice, and learn from experienced VPS users.
- Online Courses and Tutorials: Several online courses and tutorials are available on platforms like Udemy, Coursera, and YouTube. These resources provide structured learning paths on various aspects of VPS administration.
VPS for Advanced Users: Vps Dedicated Server
For users who demand more control and flexibility, VPS hosting offers a range of advanced features and optimization techniques. These options empower you to tailor your VPS environment to meet specific application needs and maximize performance.
Advanced VPS Configurations and Optimization Techniques, Vps dedicated server
Beyond basic configurations, advanced VPS users can fine-tune their systems for optimal performance. This involves understanding and manipulating various server settings, such as:
- CPU and Memory Allocation: Adjusting the allocation of CPU cores and RAM to individual applications can ensure critical processes receive the resources they need.
- Storage Optimization: Employing techniques like RAID configurations and SSD drives can significantly enhance data access speeds and overall system performance.
- Kernel Tuning: Optimizing kernel parameters can improve system responsiveness and efficiency, particularly for resource-intensive applications.
- Network Optimization: Configuring network settings, such as MTU size and buffer settings, can enhance network throughput and minimize latency.
Containerization Technologies for Application Deployment
Containerization technologies like Docker provide a powerful approach to deploying and managing applications on VPS servers. Docker containers encapsulate applications and their dependencies, ensuring consistent execution across different environments.
- Simplified Deployment: Docker simplifies application deployment by packaging all required components into a single container image. This eliminates the need for complex manual configurations and ensures consistent application behavior across different environments.
- Resource Isolation: Containers provide a level of resource isolation, preventing applications from interfering with each other or the host system. This improves stability and security.
- Scalability and Flexibility: Docker containers can be easily scaled up or down to meet changing demands, making them ideal for applications with fluctuating workloads.
- Microservices Architecture: Docker facilitates the adoption of microservices architecture, allowing complex applications to be broken down into smaller, independent services that can be developed, deployed, and scaled independently.
Managing Complex VPS Environments
Advanced VPS users often manage complex environments with multiple applications and services. Effective management involves:
- Automation: Automating repetitive tasks through scripting and configuration management tools reduces manual effort and ensures consistency.
- Monitoring and Logging: Implementing comprehensive monitoring and logging systems provides insights into system performance, application health, and potential security issues.
- Security Measures: Implementing robust security measures, such as firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and regular security updates, is crucial for protecting VPS environments from threats.
- Backup and Disaster Recovery: Regularly backing up data and configuring disaster recovery plans ensures business continuity in case of system failures or data loss.
Leveraging VPS Resources for High-Performance Computing and Data Analysis
VPS servers provide a platform for demanding tasks like high-performance computing (HPC) and data analysis. By utilizing dedicated resources and advanced configurations, VPS users can achieve significant performance gains.
- Scientific Simulations: VPS servers can be used to run complex scientific simulations and models, enabling researchers to explore scientific phenomena and develop new solutions.
- Data Analysis and Machine Learning: VPS resources can be leveraged for large-scale data analysis, machine learning, and artificial intelligence tasks, enabling insights from vast datasets.
- Financial Modeling and Trading: VPS servers provide a stable and reliable platform for running financial models, executing trading strategies, and processing high volumes of market data.
Epilogue
The world of VPS dedicated servers is vast and constantly evolving. As technology advances, VPS dedicated servers continue to offer a powerful and adaptable platform for various online endeavors. By carefully considering your needs and exploring the options available, you can leverage the power of VPS dedicated servers to achieve your online goals.
A VPS dedicated server offers a more controlled environment than shared hosting, providing you with dedicated resources and root access. However, if you’re looking for even greater flexibility and scalability, an online cloud server might be the better choice. Cloud servers offer pay-as-you-go pricing and the ability to quickly scale up or down your resources as needed.
Ultimately, the best option for you will depend on your specific needs and budget.