AWS VPS servers, also known as Virtual Private Servers, offer a powerful and flexible solution for businesses and individuals looking to host websites, applications, and other online services. These servers provide a dedicated environment within the AWS cloud, offering greater control and customization compared to shared hosting options.
With AWS VPS servers, you can leverage the vast resources and scalability of the AWS infrastructure while enjoying the benefits of a dedicated server environment. This allows you to optimize performance, manage resources efficiently, and ensure high availability for your applications.
Security Considerations for AWS VPS Servers
AWS VPS servers offer a flexible and scalable platform for various applications. However, they also present unique security challenges due to the shared nature of the infrastructure. Understanding these risks and implementing appropriate security measures is crucial to protecting your data and applications.
Potential Security Risks, Aws vps server
AWS VPS servers, while offering significant advantages, come with inherent security risks that need careful consideration. Here are some of the most common threats:
- Vulnerabilities in Operating System and Software: Outdated software or unpatched vulnerabilities can expose your server to attacks. Regular updates and patching are essential to mitigate these risks.
- Misconfigured Security Settings: Incorrectly configured firewalls, access control lists, or other security settings can create unintended vulnerabilities, allowing unauthorized access to your server.
- Unsecured Network Connections: Using insecure protocols or weak passwords for network connections can compromise your server’s security.
- Malware and Viruses: Your server can be infected with malware or viruses through various means, such as phishing emails, malicious websites, or compromised software.
- Denial-of-Service Attacks (DoS): DoS attacks aim to overload your server with traffic, making it unavailable to legitimate users. This can disrupt your services and impact your business operations.
- Data Breaches: Unauthorized access to your server can lead to data breaches, exposing sensitive information such as customer data, financial records, or intellectual property.
Best Practices for Securing an AWS VPS Server
Securing an AWS VPS server requires a multi-layered approach, encompassing various security measures. Here are some best practices:
- Implement a Strong Firewall: A firewall acts as a barrier between your server and the external network, blocking unauthorized access. Configure your firewall to allow only necessary traffic and block all other connections.
- Use Strong Passwords and Two-Factor Authentication: Employ strong, unique passwords for all accounts and enable two-factor authentication (2FA) for added security.
- Keep Software Up to Date: Regularly update your operating system, applications, and security software to patch vulnerabilities and protect against known exploits.
- Limit User Privileges: Grant only necessary permissions to users and applications, adhering to the principle of least privilege. This minimizes the potential damage from a compromised account.
- Monitor Security Logs: Regularly review security logs to detect suspicious activity and potential security breaches. Analyze logs for patterns and anomalies that could indicate malicious behavior.
- Implement Security Monitoring Tools: Use security monitoring tools to continuously scan for vulnerabilities, detect threats, and provide real-time alerts. These tools can help identify and respond to security incidents quickly.
- Backup Data Regularly: Regular backups are crucial for data recovery in case of a security breach or disaster. Store backups securely and ensure they are regularly tested for recoverability.
Security Measures and their Impact
| Security Measure | Impact on Server Security |
|---|---|
| Firewall | Blocks unauthorized access to the server, preventing malicious connections and attacks. |
| Strong Passwords and 2FA | Reduces the risk of unauthorized access to accounts, enhancing user authentication and protection. |
| Software Updates | Patches vulnerabilities and exploits, preventing attackers from exploiting weaknesses in the operating system and applications. |
| Limited User Privileges | Minimizes the potential damage from a compromised account by restricting user permissions and access. |
| Security Logs | Provides valuable insights into server activity, enabling detection of suspicious behavior and potential security breaches. |
| Security Monitoring Tools | Continuously scan for vulnerabilities, detect threats, and provide real-time alerts, enhancing threat detection and response capabilities. |
| Data Backups | Enables data recovery in case of a security breach or disaster, minimizing data loss and downtime. |
AWS VPS Server Pricing and Cost Management
AWS VPS server pricing is a complex topic, influenced by various factors, including instance type, usage, and data transfer. Understanding the pricing structure and implementing cost management strategies are crucial for optimizing your AWS VPS server expenses. This section delves into the pricing models, cost management techniques, and the impact of various pricing factors on overall cost.
Pricing Models and Cost Factors
AWS VPS server pricing is based on a pay-as-you-go model, meaning you only pay for the resources you use. However, the cost can vary significantly depending on the instance type, usage duration, data transfer volume, and other factors.
- Instance Type: AWS offers a wide range of instance types, each with different CPU, memory, and storage configurations. Choosing the right instance type is crucial for balancing performance and cost. For instance, a high-performance instance with a large amount of RAM and CPU will cost more than a basic instance.
- Usage Duration: The longer you use an instance, the more you pay. AWS offers various pricing options, including hourly, monthly, and reserved instances, which provide discounts for long-term commitments.
- Data Transfer: Data transfer charges apply for transferring data in and out of your AWS VPS server. These charges vary depending on the region and the amount of data transferred.
- Storage: AWS provides different storage options, including EBS (Elastic Block Storage) and S3 (Simple Storage Service). The cost of storage varies depending on the type of storage, the amount of storage used, and the data access frequency.
Cost Management Strategies
Optimizing AWS VPS server expenses involves a combination of strategies, including choosing the right instance type, utilizing reserved instances, monitoring usage, and optimizing application performance.
- Choose the Right Instance Type: Selecting an instance type that meets your application’s requirements without overprovisioning resources is crucial. Using AWS’s EC2 Instance Selector tool can help you choose the most cost-effective instance type for your needs.
- Utilize Reserved Instances: Reserved instances offer discounts for long-term commitments to specific instance types. If you know your application’s resource requirements will remain consistent, reserving instances can significantly reduce your costs.
- Monitor Usage: Regularly monitoring your AWS VPS server usage helps identify areas for optimization. Tools like AWS CloudWatch provide detailed metrics on CPU, memory, and disk usage, allowing you to identify idle resources or potential bottlenecks.
- Optimize Application Performance: Optimizing your application’s performance can reduce resource consumption and lower costs. Techniques like code optimization, database tuning, and caching can significantly improve efficiency.
- Utilize Spot Instances: Spot instances are spare EC2 instances available at a discounted rate. While they can be interrupted, they are ideal for workloads that are flexible or can tolerate interruptions.
Pricing Model Impact on Cost
The following table illustrates the impact of different pricing models on overall cost:
| Pricing Model | Description | Impact on Cost |
|---|---|---|
| On-Demand Instances | Pay-as-you-go pricing for instances. | Flexible, but can be expensive for long-term use. |
| Reserved Instances | Discounts for long-term commitments to specific instance types. | Cost-effective for predictable workloads, but less flexible. |
| Spot Instances | Discounted instances available when spare capacity is available. | Significantly lower cost, but instances can be interrupted. |
Alternatives to AWS VPS Servers

AWS VPS servers offer a robust and reliable cloud computing solution, but they’re not the only option available. Various cloud providers offer similar services with unique features and pricing models. Exploring these alternatives can help you find the best fit for your specific needs and budget.
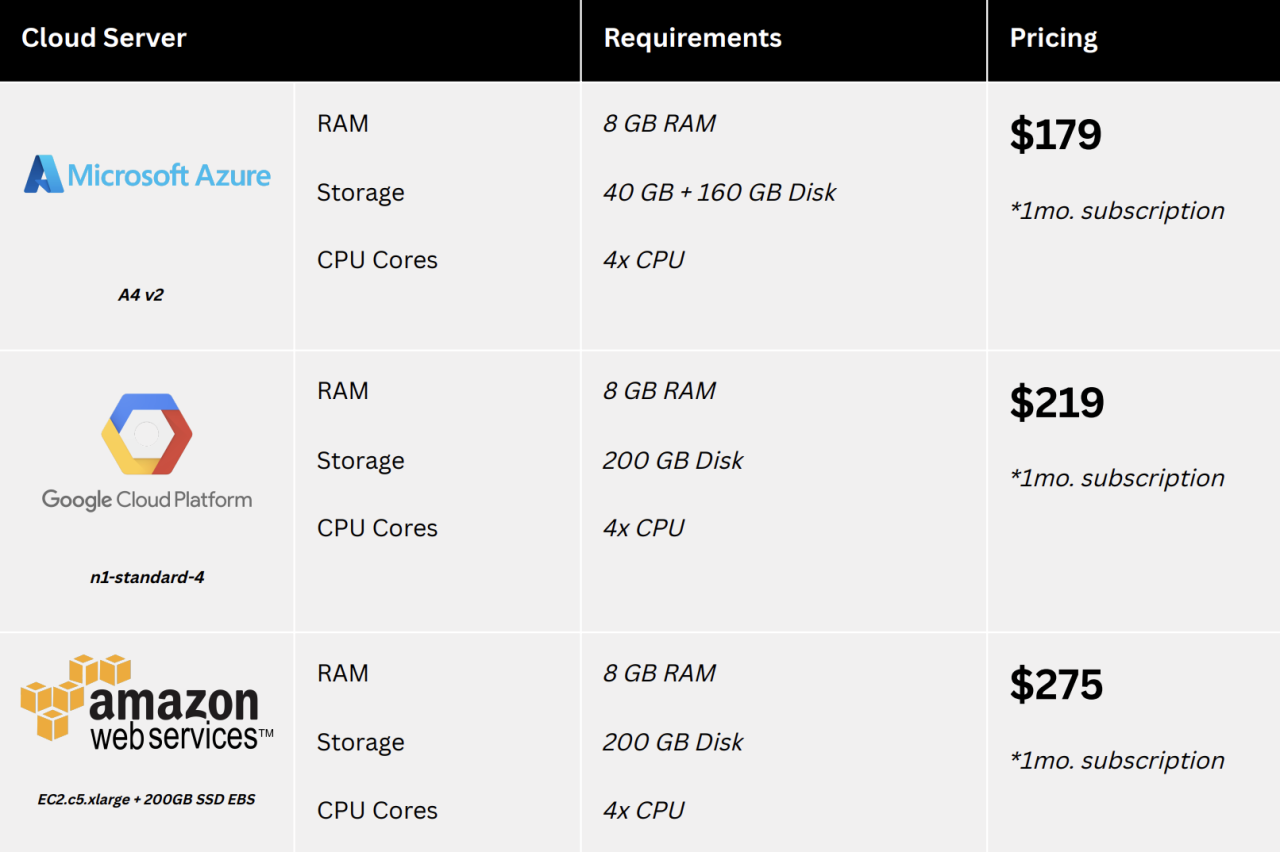
Comparison of Cloud Server Providers
This section compares and contrasts AWS VPS servers with alternative cloud server solutions from other providers. It discusses the advantages and disadvantages of each option based on factors like pricing, features, and support.
| Provider | Pricing | Features | Support | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AWS | Pay-as-you-go, Reserved Instances, Spot Instances | Compute, Storage, Networking, Databases, Security, Monitoring, Management | 24/7 technical support, documentation, community forums | Extensive features, global infrastructure, scalability, security, robust support | Can be complex, pricing can be unpredictable, high learning curve |
| Microsoft Azure | Pay-as-you-go, Reserved Instances, Spot Instances | Compute, Storage, Networking, Databases, Security, Monitoring, Management | 24/7 technical support, documentation, community forums | Integration with Microsoft products, strong security, comprehensive features | Can be expensive, less flexible than AWS, limited open-source support |
| Google Cloud Platform (GCP) | Pay-as-you-go, Committed Use Discounts, Preemptible VMs | Compute, Storage, Networking, Databases, Security, Monitoring, Management | 24/7 technical support, documentation, community forums | High performance, innovative features, competitive pricing, strong AI/ML capabilities | Smaller ecosystem than AWS, less mature than AWS, limited support for legacy applications |
| DigitalOcean | Simple, predictable pricing, Droplets (VPS instances) | Compute, Storage, Networking, Databases, Security, Monitoring, Management | 24/7 technical support, documentation, community forums | Easy to use, affordable, good for small businesses and startups | Limited features compared to larger providers, less mature infrastructure |
| Linode | Simple, predictable pricing, Linodes (VPS instances) | Compute, Storage, Networking, Databases, Security, Monitoring, Management | 24/7 technical support, documentation, community forums | Affordable, reliable, good for developers and small businesses | Limited features compared to larger providers, less mature infrastructure |
Ultimate Conclusion
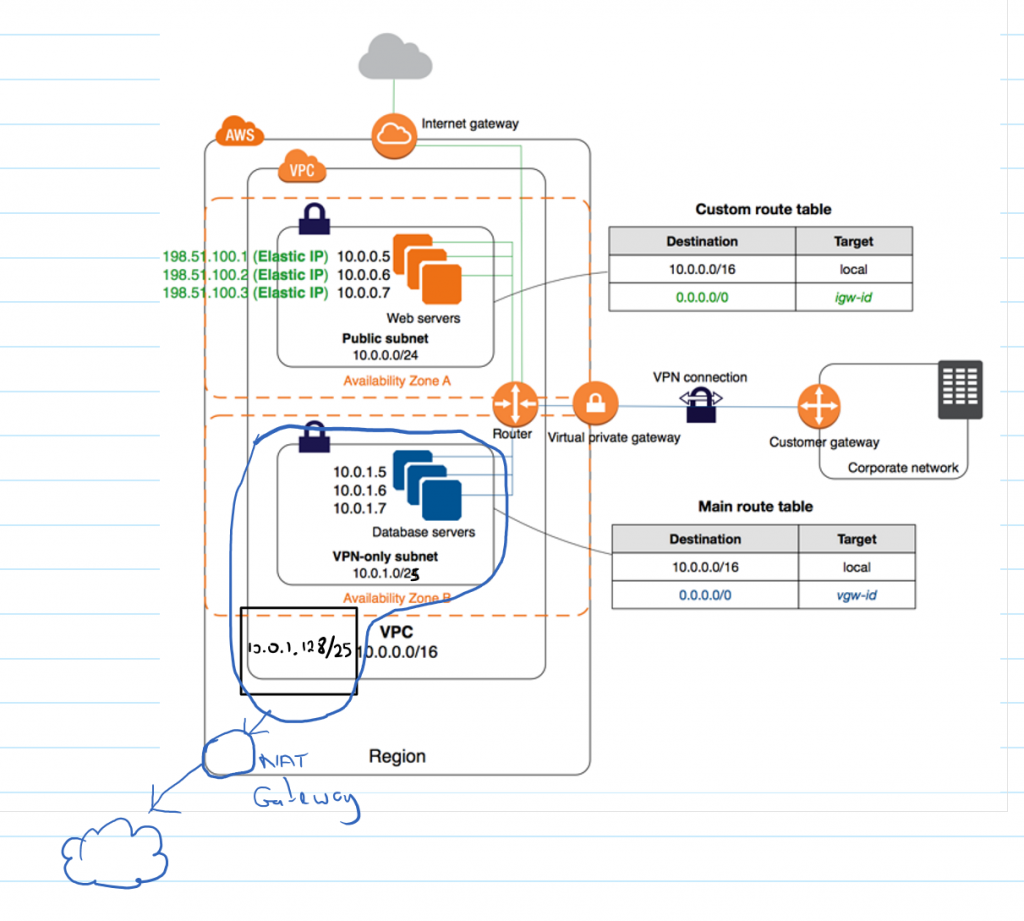
In conclusion, AWS VPS servers provide a compelling solution for those seeking a balance between the control of a dedicated server and the scalability and flexibility of the cloud. By understanding the various types, configurations, and benefits of AWS VPS servers, you can make informed decisions about your hosting needs and leverage the power of AWS to achieve your business goals.